The H5N1 pandemic, a global health crisis, has sparked widespread concern and spurred scientific research. This highly pathogenic avian influenza virus poses significant risks to both humans and poultry, with implications for public health and economic stability.
Since its emergence in 1996, the H5N1 virus has spread rapidly across continents, causing severe respiratory illness and mortality in birds. Human infections, though less common, have occurred, raising alarms about the potential for a human pandemic.
Overview of H5N1 Pandemic
The H5N1 virus, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, has raised significant concerns due to its potential to cause a global pandemic. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the H5N1 pandemic, encompassing its origins, transmission, symptoms, prevention, public health impact, scientific research, global collaboration, and future preparedness.
Define H5N1 virus and its characteristics, H5n1 pandemic
The H5N1 virus belongs to the family of influenza A viruses that primarily infect birds. It is characterized by its ability to cause severe respiratory illness and high mortality rates in both birds and humans. The virus has a segmented RNA genome, which allows for rapid genetic mutations and adaptations, contributing to its pandemic potential.
Explain the history and origin of the H5N1 pandemic
The H5N1 virus was first identified in 1996 in Hong Kong during an outbreak among poultry. Since then, it has spread to multiple countries, causing sporadic outbreaks in both poultry and humans. The virus has evolved over time, acquiring mutations that have increased its transmissibility and virulence.
In 2003, the H5N1 virus caused a major outbreak in Southeast Asia, resulting in significant human infections and fatalities.
Transmission and Spread: H5n1 Pandemic
Describe the modes of transmission of H5N1 virus
The H5N1 virus primarily transmits through direct contact with infected birds or their secretions. Humans can become infected through:
- Contact with infected poultry or their feces
- Inhalation of aerosolized virus from infected birds
- Consumption of undercooked poultry products
Explain the factors influencing the spread of H5N1 virus
The spread of the H5N1 virus is influenced by several factors, including:
- Poultry farming practices:Intensive poultry farming and close proximity of birds can facilitate the spread of the virus.
- Wild bird migration:Migratory birds can carry the virus over long distances, contributing to its geographic spread.
- Environmental factors:Temperature and humidity can affect the survival and transmission of the virus.
- Human behavior:Close contact with infected birds or consumption of undercooked poultry products can increase the risk of human infection.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
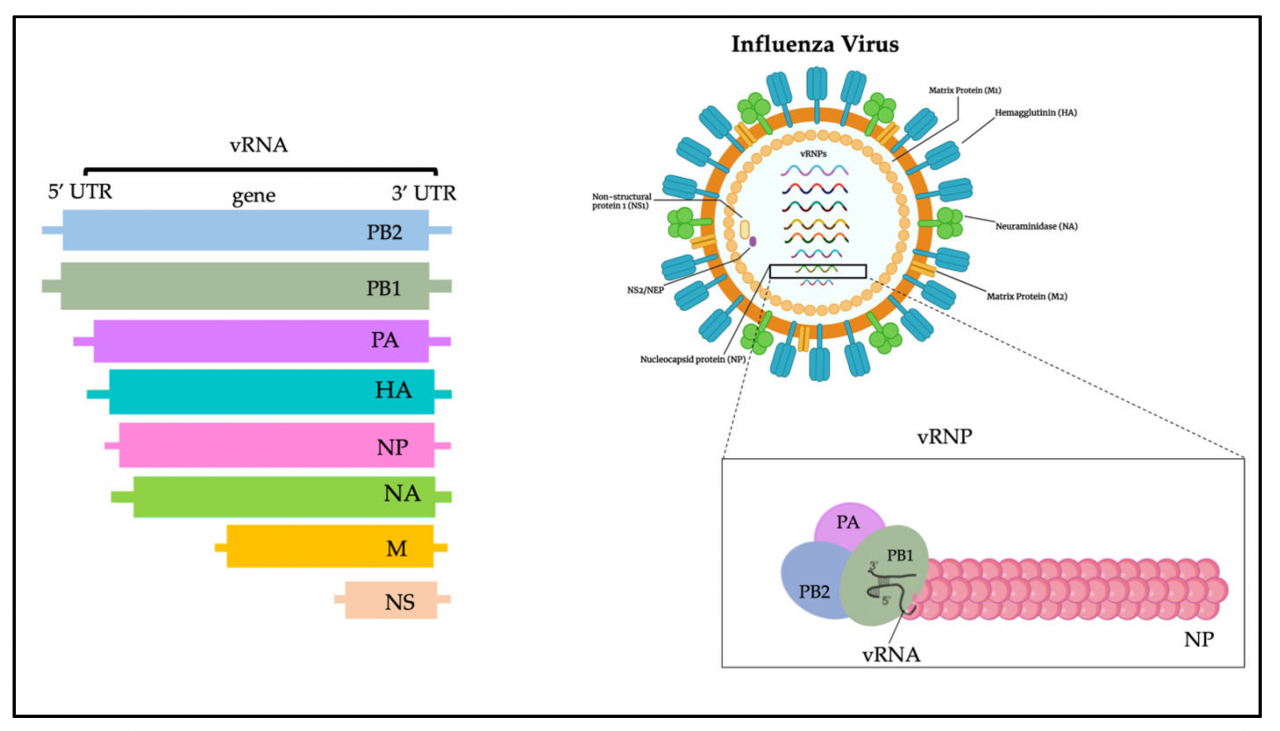
List the common symptoms of H5N1 infection
Symptoms of H5N1 infection in humans can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Muscle aches
- Headache
- Shortness of breath
- Pneumonia
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Explain the methods for diagnosing H5N1 infection
Diagnosis of H5N1 infection is typically based on:
- Clinical symptoms:Healthcare providers may suspect H5N1 infection based on the patient’s symptoms and exposure history.
- Laboratory tests:Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and viral culture can confirm the presence of the H5N1 virus.
- Serological tests:Antibody tests can detect antibodies produced by the body’s immune system in response to H5N1 infection.
Prevention and Control
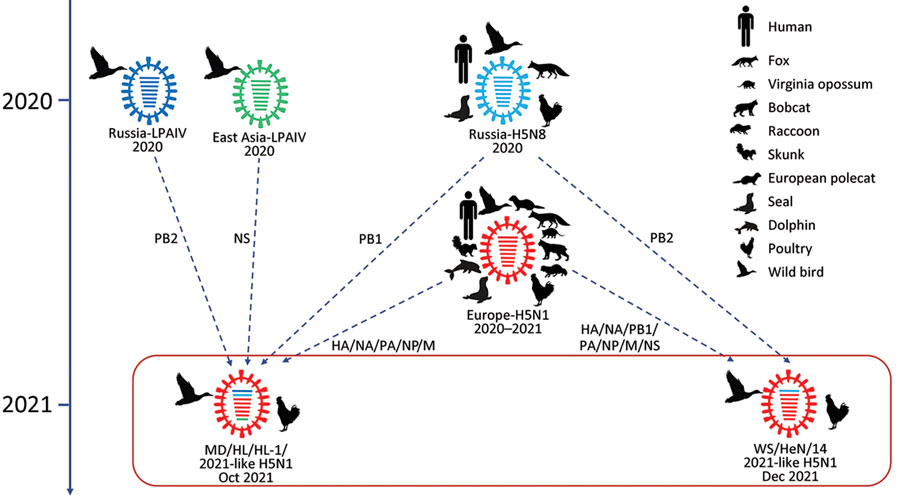
Discuss the measures for preventing H5N1 infection
Prevention of H5N1 infection involves implementing comprehensive measures, including:
- Poultry vaccination:Vaccinating poultry can reduce the spread of the virus among birds and prevent human infections.
- Biosecurity measures:Strict biosecurity measures in poultry farms, including proper sanitation and isolation of infected birds, can help control the spread of the virus.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE):Healthcare workers and individuals working with poultry should wear appropriate PPE, such as masks, gloves, and gowns, to prevent exposure to the virus.
- Public health education:Raising awareness about the risks of H5N1 infection and promoting good hygiene practices can help reduce the spread of the virus.
Explain the role of vaccines and antiviral medications in controlling H5N1
Vaccines and antiviral medications play a crucial role in controlling H5N1 infection:
- Vaccines:H5N1 vaccines are available for individuals at high risk of exposure, such as poultry workers and healthcare professionals. Vaccination can provide protection against infection or reduce the severity of symptoms.
- Antiviral medications:Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, can be used to treat H5N1 infection and reduce the risk of severe complications.
End of Discussion
Addressing the H5N1 pandemic requires a multifaceted approach involving global collaboration, scientific research, and public health measures. By sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise, we can enhance our preparedness for future pandemic threats and safeguard the health of both humans and animals.